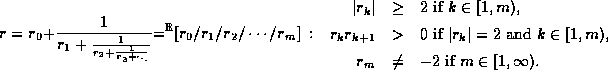
Next: 2.15.8 Generalized Interval Arithmetic
Up: 2.15 Real Representations
Previous: 2.15.6 Redundant Decimal Expansions
As with the conventional continued fraction representation,
each real number is represented by a continued fraction.
Each term may now be positive or negative:
Negative numbers can be represented immediately.
An interval variant of Euclid's algorithm is used to determine
the sequence of terms for a given real number.
Software designers have used this approach for real arithmetic
[69].
Next: 2.15.8 Generalized Interval Arithmetic
Up: 2.15 Real Representations
Previous: 2.15.6 Redundant Decimal Expansions